Henry Hudson was a prominent explorer whose voyages in the early 17th century significantly contributed to the mapping of North America. His expeditions not only opened new trade routes but also laid the groundwork for future explorations and settlements. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating life of Henry Hudson, exploring his journeys, discoveries, and the lasting impact he had on exploration and cartography.
Throughout his career, Hudson undertook several notable voyages under the auspices of various European nations, including England and the Netherlands. His most famous expedition led to the discovery of the river that now bears his name, the Hudson River, and the bay that is known as Hudson Bay. These discoveries were pivotal in shaping the geographical understanding of North America during the age of exploration.
This article will provide an in-depth look at Henry Hudson's life, his expeditions, and the historical context in which he operated. By examining his achievements and challenges, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of why Hudson remains a significant figure in the annals of exploration.
Table of Contents
- Biography of Henry Hudson
- Early Life and Background
- Hudson's Major Expeditions
- First Voyage: The Search for a Northeast Passage
- Second Voyage: The Quest for a Northwest Passage
- Third Voyage: Discovery of the Hudson River
- Legacy and Impact of Hudson's Discoveries
- Conclusion
Biography of Henry Hudson
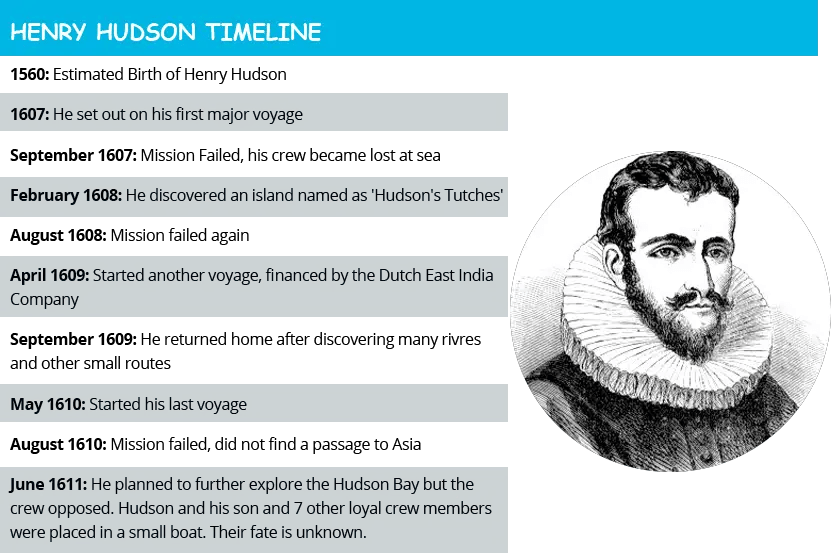
Henry Hudson was born around 1565 in England. Little is known about his early life, but he is believed to have been involved in maritime activities from a young age. His experience and knowledge of navigation made him a suitable candidate for several exploratory missions.
Personal Data and Biodata
| Name | Henry Hudson |
|---|---|
| Born | Circa 1565 |
| Nationality | English |
| Profession | Explorer |
| Notable Achievements | Discovery of Hudson River and Hudson Bay |
| Died | 1611 (disappeared) |
Early Life and Background
While the exact details of Hudson's early life remain sparse, records suggest that he was born into a family of explorers or mariners, which likely influenced his career choice. He developed a keen interest in navigation, eventually obtaining the skills necessary to command ships on exploratory voyages.
Hudson's early career included several voyages to the Arctic regions in search of a Northeast Passage to Asia. His experiences during these expeditions shaped his understanding of navigation and exploration, paving the way for future significant journeys.
Hudson's Major Expeditions
First Voyage: The Search for a Northeast Passage
In 1607, Hudson embarked on his first major voyage aboard the ship "Hopewell." Sponsored by English merchants, his mission was to find a Northeast Passage to the riches of Asia. Although he faced treacherous weather and challenging sea conditions, Hudson's determination led him to explore the coasts of Greenland and northern Russia.
Despite not achieving his goal of a direct route to Asia, Hudson's observations and mapping of these regions contributed valuable knowledge to European cartography.
Second Voyage: The Quest for a Northwest Passage
In 1609, Hudson embarked on his second expedition, this time under the Dutch East India Company. His objective was to find a Northwest Passage to Asia through North America. Hudson navigated the eastern coast of Canada and eventually discovered the river that would later bear his name—the Hudson River.
During this voyage, Hudson established relationships with indigenous peoples and collected valuable information about the land, which would prove crucial for future colonization efforts.
Third Voyage: Discovery of the Hudson River
Hudson's third and final voyage took place in 1610, when he entered what is now known as Hudson Bay. This expedition was marked by challenges, including harsh weather conditions and dwindling supplies. Despite these difficulties, Hudson's exploration of the bay and its surrounding areas expanded European knowledge of North America's geography.
However, tensions arose among Hudson's crew, leading to a mutiny in 1611. Hudson and a small group of loyal crew members were abandoned in the bay, and he was never seen again, leaving behind a legacy as one of the early pioneers of North American exploration.
Legacy and Impact of Hudson's Discoveries
Henry Hudson's expeditions had a profound impact on the understanding of North America and the development of future settlements. His discoveries of the Hudson River and Hudson Bay paved the way for Dutch and later British colonization of the region.
- Hudson River: The river became a vital trade route, facilitating commerce and transportation.
- Hudson Bay: The bay served as a key location for fur trading, significantly influencing the economy of the region.
- Cultural Exchange: Hudson's interactions with indigenous peoples fostered cultural exchanges that shaped the early colonial landscape.
Additionally, Hudson's maps and navigational accounts provided invaluable resources for future explorers, solidifying his place in the history of exploration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Henry Hudson was a pivotal figure in the age of exploration, whose voyages transformed the understanding of North America. His relentless pursuit of new trade routes and his discoveries of the Hudson River and Hudson Bay laid the foundation for future exploration and colonization.
As we reflect on Hudson's legacy, it is essential to recognize the complexities of his journeys and the impact they had on both the European world and indigenous communities. If you found this article insightful, feel free to leave a comment, share it with others, or explore more articles on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more engaging content on history and exploration!